
Revision 1.0
31 July 2013

Description:
This CFP Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) defines the CFP2 form factor of an optical transceiver to support 40Gbit/s and 100Gbit/s interfaces for Ethernet, Telecommunication and other applications. The members of the CFP MSA have authored this document to provide an industry standard form factor for new and emerging high speed communications interfaces. Specifications provided in this document are given as a “delta” to the CFP MSA Hardware Specification Rev. 1.4, June 7, 2010.
CONTENTS
CFP2 HARDWARE SIGNALING PINS 13
CFP2 Bail Latch Color Coding and Labeling 57
Draft | Date | Revised Items |
0.0 | Nov. 30, 2012 | Initial draft, based on CFP2 Baseline Design, Release 1 |
0.1 | Dec. 14, 2012 | Edits from CFP MSA System OEM Reviewers comments - |
0.2 | Mar. 14, 2013 | Added Table 2-5: Timing Parameters for CFP Hardware Signal Pins. Add Power Class 5 & 6 in Table 4-1 Voltage power supply Added future high speed electrical interface in Section 4.4. Changed Figure 4-1 to include common mode impedance termination. Changed REFCLK alternatives in Table 4-4 to be in line with what are specified in the MDIO specification. |
0.3 | Apr. 25, 2013 | Added Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2 Modified Figure 5-7, Figure 5-8 and Figure 5-10 according to the latest published CFP2 baseline drawing Added maximum weight value in Table 5-1 Replaced TBD with actual values in Table 5-2 |
1.0 | Jul. 31, 2013 | Added Table 5-7 & Table 5-10 for multi-port application |
Table 2-2: CFP2 Module Power Classes defined by Hardware Interlock 15
Table 2-3: Hardware Alarm Pins 16
Table 2-4: Management Interface Pins (MDIO) 17
Table 2-5: Timing Parameters for CFP Hardware Signal Pins 17
Table 4-1 Voltage power supply 23
Table 4-2: Optional Reference Clock Characteristics 28
Table 4-3: Optional Transmitter & Receiver Monitor Clock Characteristics 30
Table 4-4: CFP2 Module Clocking Signals 19
Table 5-1: CFP2 Mechanical Characteristics 43
Table 5-2: CFP2 Module Insertion, Extraction Forces 44
Table 5-3: Optical Connectors 28
Table 5-4 CFP2 Host Connector Assembly 29
Table 5-5: CFP2 N x 25 Gbit/s Pin-Map 63
Table 5-6: CFP2 10 x 10 Gbit/s Pin-Map 51
Table 5-7: CFP2 CFP2 Multi-Port Pin-Map 51
Table 5-8: CFP2 Bottom Row Pin Description for N x 25 Gbit/s applications Error! Bookmark not
defined.
Table 5-9: CFP2 Bottom Row Pin Description for 10 x 10 Gbit/s applications 63
Table 5-10: CFP2 Bottom Row Pin Description for Multi-Port applications 63
Table 5-11: CFP2 Bail Latch Color Coding 64
Figure 1-1: CFP2 Functional Block Diagram 8
Figure 2-1: Reference +3.3V LVCMOS Output Termination 25
Figure 2-2: Reference MDIO Interface Termination 25
Figure 4-1: High Speed I/O for Data and Clocks 25
Figure 4-2: CFP2 Module Optional Loopback Orientation 27
Figure 4-3: Example of clocking for 4 x 25 Gbit/s CFP2 applications 20
Figure 4-4: Example of clocking for 10 x 10 Gbit/s CFP2 applications 20
Figure 5-1: CFP2 Module & CFP2 Module Mated in Host Dual Port System 21
Figure 5-2: Host Cage System and Mounting Method Overview 22
Figure 5-3: CFP2 Module Plug Connector Assembly 37
Figure 5-4: CFP2 Dual Port Host Connector Cover Assembly 37
Figure 5-5: CFP2 Host Connector Assembly 39
Figure 5-6: CFP2 Pin Map Connector Engagement 39
Figure 5-7: CFP2 Module Dimension Overview 41
Figure 5-8: Riding Heat Sink 45
Figure 5-9: Host Cage Top Surface Opening 27
Figure 5-10: CFP2 Optical Connector Position 28
Figure 5-11: CFP2 Connector Pin Map Orientation 29
Figure 5-12: CFP2 Module Label Recess 64
CFP MSA Hardware Specification, Revision 1.4, June 7, 2010.
OIF-CEI-3.0, http://www.oiforum.com/public/documents/OIF_CEI_03.0.pdf
IEEE P802.3bm, 40Gbit/s and 100Gbit/s Operation Over Fiber Optic Cables Task Force, http://www.ieee802.org/3/bm/index.html
ITU-T Recommendation G.709 (2012) Interfaces for the Optical Transport Network (OTN).
IEEE Std 802.3TM-2012, Annexes 83A, 83B, and 86A.
ITU-T Recommendation G.707 (2003) Network node interface for the synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH).
CFP MSA Management Interface Specification, Version 2.2, July 01, 2013.
IEEE Std 802.3TM-2012, Cl. 45, Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) Interface.
SFF Committee INF-8077i 10 Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggable Module
SFF Committee SFF-8431 Specifications for Enhanced Small Form Factor Pluggable Module SFP+
![]()
![]()
This CFP Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) defines the CFP2 form factor of an optical transceiver which can support 10Gbit/s, 40Gbit/s, 100Gbit/s and 400Gbit/s interfaces for Ethernet, ITU-T OTN and other applications. Specifications provided in this document are given as a “delta” to the CFP MSA Hardware Specification Rev. 1.4 [1].
The CFP2 electrical interface will vary by application, but the nominal signaling lane rate is 25Gbit/s per lane and documentation is provided in OIF CEI-28G-VSR [2], CAUI-4 [3], and OTL4.4 [4] electrical interface specifications. The CFP2 electrical interface can also optionally support a nominal signaling lane rate of 10Gbit/s and documentation is provided in CAUI [5], XLAUI [5], CPPI [5], XLPPI [5], OTL4.10 [4], OTL3.4[4] and STL256.4[6]. The CFP2 module may be used to support single mode and multimode fiber optics.
The CFP2 also support 50Gbit/s per lane signaling rate which is anticipated to be specified in the OIF CEI-56G-VSR IA.
The CFP2 modules and the host system are hot-pluggable. The module or the host system shall not be damaged by insertion or removal of the module.
CFP MSA is an acronym for 100G1 Form factor Pluggable Multi-Source Agreement.
Per specifications given in CFP MSA [1].
![]()
1 C = 100 in Roman numerals; Centum
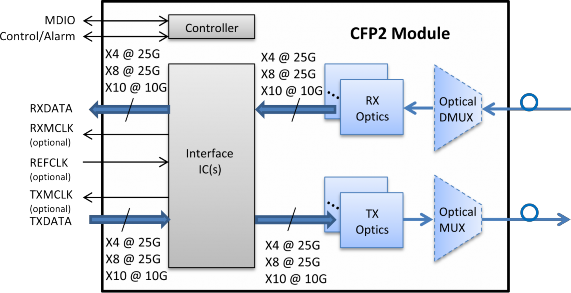
Figure 1-1: CFP2 Functional Block Diagram
* Other supported RXDATA and TXDATA bit rates include x8 @ 50Gbit/s.
The CFP2 module is a hot pluggable form factor designed for optical networking applications. The module size has been chosen to accommodate a wide range of power dissipations and applications. The module electrical interface has been generically specified to allow for supplier-specific customization around various “4 x 25Gbit/s” interfaces, but can support 8x25Gbit/s, 10x10Gbit/s, and 8x50Gbit/s.
Per specifications given in CFP MSA Hardware Specification, Revision 1.4, June 7, 2010 [1].
![]()
![]()
The control and status reporting functions between a host and a CFP2 module use non-data control and status reporting pins on the 104-pin connector. The control and status reporting pins work together with the MDIO interface to form a complete HOST-CFP2 management interface. The status reporting pins provide status reporting. There are six (6) Hardware Control pins, five (5) Hardware Alarm pins, and six (6) pins dedicated to the MDIO interface. Specification of the CFP2 hardware signaling pins are given in Ref. [1] with the following changes listed in this section.
The CFP2 Module supports real-time control functions via hardware pins, listed in
Table 2-1. Specifications of the CFP2 hardware control pins are given in Ref. [1], with the following changes listed below.
Pin # | Symbol | Description | I/O | Logic | “H” | “L” | Pull-up /down |
Programmable Control 1 | |||||||
17 | PRG_CNTL1 | MSA Default: TRXIC_RSTn, TX & RX ICs reset, | I | 3.3V LVCMOS | Pull – Up2 | ||
"0": reset, "1"or NC: enabled | |||||||
per CFP MSA MIS Ref. [7] | |||||||
18 | PRG_CNTL2 | Programmable Control 2 MSA Default: Hardware Interlock LSB | I | 3.3V LVCMOS | Pull – Up2 | ||
19 | PRG_CNTL3 | Programmable Control 3 MSA Default: Hardware Interlock MSB | I | 3.3V LVCMOS | Pull – Up2 | ||
24 | TX_DIS | Transmitter Disable | I | 3.3V LVCMOS | Disable | Enable | Pull – Up2 |
26 | MOD_LOPWR | Module Low Power Mode | I | 3.3V LVCMOS | Low Power | Enable | Pull – Up2 |
28 | MOD_RSTn | Module Reset, Active Low (invert) | I | 3.3V LVCMOS | Enable | Reset | Pull – Down3 |
2Pull-Up resistor (4.7 kOhm to 10 kOhm) is located within the CFP2 module
3Pull-Down resistor (4.7 kOhm to 10 kOhm) is located within the CFP2 module
Hardware Control Pins: Functional Description
Per specifications given in CFP MSA Hardware Specification, Revision 1.4, June 7, 2010 [1] except as noted below.
Programmable Controls (PRG_CNTLs)
Hardware Interlock
Table 2-2: CFP2 Module Power Classes defined by Hardware Interlock
Hardware Interlock Description | Power Class | CFP2 Module Power Dissipation W | |
MSB | LSB | ||
0 | 0 | 1 | ≤ 3 |
0 | 1 | 2 | ≤ 6 |
1 | 0 | 3 | ≤ 9 |
1 | 1 | > 4 | > 9 |
The CFP2 Module supports alarm hardware pins as listed in Table 2-3. Specifications of the CFP2 hardware alarm pins are given in Reference [1].
Table 2-3: Hardware Alarm Pins
Pin # | Symbol | Description | I/O | Logic | “H” | “L” | Pull-up /down |
20 | PRG_ALRM1 | Programmable Alarm 1 MSA Default: HIPWR_ON | O | 3.3V LVCMOS | Active High per CFP MSA MIS Ref. [7] | ||
21 | PRG_ALRM2 | Programmable Alarm 2 MSA Default: MOD_READY, Ready state has been reached | O | 3.3V LVCMOS | |||
22 | PRG_ALRM3 | Programmable Alarm 3 MSA Default: MOD_FAULT | O | 3.3V LVCMOS | |||
25 | RX_LOS | Receiver Loss of Signal | O | 3.3V LVCMOS | Loss of Signal | OK | |
27 | MOD_ABS | Module Absent | O | 3.3V LVCMOS | Absent | Present | Pull Down2 |
Hardware Alarm Pins: Functional Description
Per specifications given in CFP MSA Hardware Specification, Revision 1.4, June 7, 2010 [1].
The CFP2 Module supports alarm, control and monitor functions via an MDIO bus. Upon module initialization, these functions are available. CFP2 MDIO electrical interface consists of six (6) pins including two (2) pins for MDC and MDIO, three (3) Physical Port Address pins, and the Global Alarm pin. MDC is the MDIO Clock line driven by the host and MDIO is the bidirectional data line driven by both the host and module depending upon the data directions. The CFP2 MDIO pins are listed in Table 2-4. Specifications of the CFP2 hardware management interface pins are given in Reference [1] with the following changes listed below.
![]()
2 Pull-Down resistor (<100 Ohm) is located within the CFP2 module. Pull-up should be located on the host.
Table 2-4: Management Interface Pins (MDIO)
Pin # | Symbol | Description | I/O | Logic | “H” | “L” | Pull-up /down |
29 | GLB_ALRMn | Global Alarm | O | 3.3V LVCMOS | OK | Alarm | |
31 | MDC | MDIO Clock | I | 1.2V LVCMOS | |||
32 | MDIO | Management Data Input Output Bi-Directional Data | I/O | 1.2V LVCMOS | |||
33 | PRTADR0 | MDIO Physical Port address bit 0 | I | 1.2V LVCMOS | per CFP MSA MIS Ref. [7] | ||
34 | PRTADR1 | MDIO Physical Port address bit 1 | I | 1.2V LVCMOS | |||
35 | PRTADR2 | MDIO Physical Port address bit 2 | I | 1.2V LVCMOS | |||
Figure 2-1: Reference +3.3V LVCMOS Output Termination
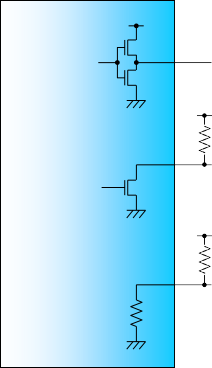
Output
+3.3V
Open Drain Output
(GLB_ALRMn)
Output w/ PDR (MOD_ABS)
<100 ohm
CFP2 module
+3.3V
4.7k ~ 10k ohm
+3.3V
4.7k ~ 10k ohm
* Per CFP MSA Hardware Specification, Revision 1.4, June 7, 2010 [1]
Figure 2-2: Reference MDIO Interface Termination3
CFP2 module
MDC
+1.2V
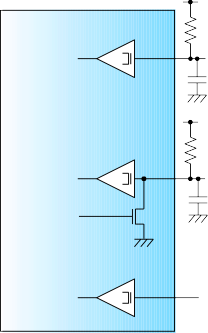
>= 250 ohm
<= 200 pF
MDIO
+1.2V
>=250 ohm
<= 200 pF
PRTADR [n]
* Per CFP MSA Hardware Specification, Revision 1.4, June 7, 2010 [1]
The above drawing, with maximum host load capacitance of 200pF, also defines the measurement set-up for module MDC timing verification
CFP2 Management Interface Hardware Description
Per specifications given in CFP MSA Hardware Specification, Revision 1.4, June 7, 2010 [1] except as noted below.
These control pins are used for the system to address all of the CFP2 ports contained within a host system. PRTADR0 corresponds to the LSB in the physical port addressing scheme. The 3-wire Physical Port
![]()
3 The MSA recommends host termination resistor value of 560 Ohms, which provides the best balance of performance for both open-drain and active tri-state driver in the module. Host termination resistor values less than 560 Ohms are allowed, to a minimum of 250 Ohms, but this degrades active driver performance. Host termination resistor values greater than 560 Ohms are allowed but this degrades open-drain driver performance.
Address lines are driven by host to set the module Physical Port Address which should match the address specified in the MDIO Frame. It is recommended that the Physical Port Addresses not be changed while the CFP2 module is powered on because this will result in unpredictable module behavior.
Hardware Signaling Pin Electrical Specifications
Per specifications given in CFP MSA Hardware Specification, Revision 1.4, June 7, 2010 [1].
Hardware Signaling Pin Timing Requirements
Timing requirements for Hardware Signaling Pins can be found in Table 2-5.
Table 2-5: Timing Parameters for CFP Hardware Signal Pins
Parameter | Symbol | Min. | Max. | Unit | Notes & Conditions |
Hardware MOD_LOPWR assert | t_MOD_LOPWR_assert | 1 | ms | Application Specific. May depend on current state condition when signal is applied. See Vendor Data Sheet | |
Hardware MOD_LOPWR deassert | t_MOD_LOPWR_deassert | ms | Value is dependent upon module start-up time. Please see register “Maximum High-Power-up Time” in CFP MSA Management Interface Specification [7] | ||
Receiver Loss of Signal Assert Time | t_loss_assert | 100 | µs | Maximum value designed to support telecom applications | |
Receiver Loss of Signal De-Assert Time | t_loss_deassert | 100 | µs | Maximum value designed to support telecom applications | |
Global Alarm Assert Delay Time | GLB_ALRMn_assert | 150 | ms | This is a logical "OR" of associated MDIO alarm & status registers. Please see CFP MSA Management Interface Specification [7] for further details | |
Global Alarm De-Assert Delay Time | GLB_ALRMn_deassert | 150 | ms | This is a logical "OR" of associated MDIO alarm & status registers. Please see CFP MSA Management Interface Specification [7] for further details | |
Management Interface Clock Period | t_prd | 250 | ns | MDC is 4 MHz or less | |
Host MDIO t_setup | t_setup | 10 | ns | ||
Host MDIO t_hold | t_hold | 10 | ns | ||
CFP MDIO t_delay | t_delay | 0 | 175 | ns | |
Initialization time from Reset | t_initialize | 2.5 | s | ||
Transmitter Disabled (TX_DIS asserted) | t_deassert | 100 | µs | Application Specific | |
Transmitter Enabled (TX_DIS de-asserted) | t_assert | 20 | ms | Time from Tx Disable pin De-asserted until CFP module enters the Tx-Turn-on State |
![]()
MODULE MANAGEMENT INTERFACE DESCRIPTION
![]()
The CFP2 module utilizes MDIO IEEE Std 802.3TM-2012 clause 45 [8] for its management interface. The CFP2 MDIO implementation is defined in a separate document entitled, “CFP MSA Management Interface Specification” [7]. When multiple CFP2 modules are connected via a single bus, a particular CFP2 module can be selected by using the Physical Port Address pins.
![]()
![]()
Per specifications given in CFP MSA Hardware Specification, Revision 1.4, June 7, 2010 [1].
POWER SUPPLIES AND POWER DISSIPATION
Voltage power supply and power dissipation
The CFP2 module power supply and maximum power dissipation specifications are defined in Table 4-1.
The inrush current on the 3.3V power supply shall be limited by the CFP2 module to assure a maximum rate of change defined in Table 4-1.
The CFP2 module shall limit the turn-off current to assure a maximum rate of change per Table 4-1.
Power Supply Noise Susceptibility
A host system will supply stable power to the module and guarantee that noise & ripple on the power supply does not exceed that defined in the table. A possible example of a power supply filtering circuit that might be used on the host system is a PI C-L-C filter. A module will meet all electrical requirements and remain fully operational in the presence of noise on the 3.3V power supply which is less than that defined in the table 4-1. The component values of power supply noise filtering circuit, such as the capacitor and inductor, must be selected such that maximum Inrush and Turn-off current does not cause voltage transients which exceed the absolute maximum power supply voltage, all specified in Table 4-1.
Table 4-1 Voltage power supply
Parameters | Symbol | Min | Typ. | Max | Unit | |
Absolute Maximum Power Supply Voltage | VCC | - | - | 3.6 | V | |
Total Power Dissipation | Class 1 | Pw | - | - | 3 | W |
Class 2 | - | - | 6 | |||
Class 3 | - | - | 9 | |||
Class 4 | - | - | 12 | |||
Class 5 | - | - | 15 | |||
Class 6 | - | - | 18 | |||
Low Power Mode Dissipation | Plow | - | - | 2 | W | |
Operating Power Supply Voltage | VCC | 3.2 | 3.3 | 3.4 | V | |
Operating Power Supply Current4 | Class 1 and 2 | ICC | - | - | 1.875 | A |
Class 3 and 4 | ICC | - | - | 3.75 | A | |
Class 5 and 6 | ICC | - | - | 5.625 | A | |
Inrush Current5 | Class 1 and 2 | I-inrush | - | - | 100 | mA/usec |
Turn-off Current | I-turnoff | -100 | - | - | mA/usec | |
Inrush Current4 | Class 3 and 4 | I-inrush | - | - | 200 | mA/usec |
Turn-off Current | I-turnoff | -200 | - | - | mA/usec | |
Inrush Current4 | Class 5 and 6 | I-inrush | - | - | 250 | mA/usec |
![]()
4 Maximum current per pin shall not exceed 500mA. Those power classes for which the maximum current per pin exceeds 500mA will require agreement from an electrical connecter supplier.
![]()
5 For modules which present a small capacitive load to the host during hot plug (C 500nF), the portion of the inrush current due to charging the capacitor can be excluded from the total inrush current which must meet the maximum limit specification.
Turn-off Current | I-turnoff | -250 | - | - | mA/usec | |
Power Supply Noise | Vrip | - | - | 2% 3% | DC – 1MHz 1 – 10MHz | |
Per specifications given in CFP MSA Hardware Specification, Revision 1.4, June 7, 2010 [1].
The CFP2 module will comply with standardized optical specifications such as the optical reaches specified in IEEE for datacom applications or in ITU-T for telecom applications. Some of the relevant reference documents are: IEEE Std. 802.3TM-2012[5], Telcordia GR-253, ITU-T G.691, ITU-T G.692, ITU-T G.693, and ITU-T G.959, ITU-T G.709 [4].
HIGH SPEED ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
The CFP2 Module high speed electrical interface supports the following configurations:
4 tx lanes + 4 rx lanes, each at 25 Gbit/s;
8 tx lanes + 8 rx lanes, each at 25 Gbit/s;
10 tx lanes + 10 rx lanes, each at 10 Gbit/s.
Following electrical interfaces may be supported in future.
4 tx lanes + 4 rx lanes, each at 50 Gbit/s;
8 tx lanes + 8 rx lanes, each at 50 Gbit/s;
The high speed electrical interface shall be AC-coupled within the CFP2 module as is shown in Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1: High Speed I/O for Data and Clocks
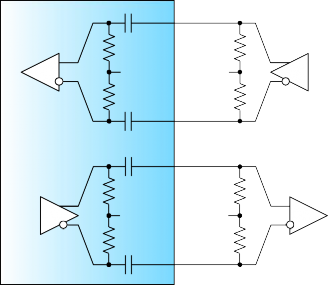
Input
50 ohm
50 ohm
VTTin
VTTout
50 ohm
50 ohm
Output
50 ohm
50 ohm
VTTout
VTTin
50 ohm
50 ohm
CFP2 module
25 Gbit/s Transmitter Data (and Clock)
The 25 Gbit/s Transmitter Data is defined in OIF CEI-28G-VSR [2]. Lane orientation and designation is specified in the pin-map tables given in Section 5.8
The specifications for 4 x 25 Gbit/s electrical interfaces for 100G Ethernet applications are currently under development in IEEE P802.3bm task force [3]. References to completed IEEE standards for these electrical interfaces will be provided in a future release of this MSA.
25 Gbit/s Receiver Data (and Clock)
The specifications for 4 x 25 Gbit/s electrical interfaces for 100G Ethernet applications are currently under development in IEEE 802.3 Working Group. References to completed IEEE standards for these electrical interfaces will be provided in a future release of this MSA.
10 Gbit/s Transmitter Data (and Clock)
The 10 Gbit/s Transmitter Data is defined in IEEE Std. 802.3TM-2012 Annex 83A for CPPI and XLPPI and Annex 83B for CAUI and XLAUI [5], or XFI in SFF INF-8077i [9] and SFI in SFF SFF-8431 [10]. Future OIF CEI-56G-VSR electrical specifications will apply. Figure 4-1 shows the recommended termination for these circuits. Alternate signaling logic are OTL3.4 and OTL4.10 which are specified in Reference [4]. Lane orientation and designation is specified in the pin-map tables given in Section 5.8.
10 Gbit/s Receiver Data (and Clock)
The 10 Gbit/s Transmitter Data is defined in IEEE Std. 802.3TM-2012 Annex 83A for CPPI and XLPPI and Annex 83B for CAUI and XLAUI [5], or XFI in SFF INF-8077i [9] and SFI in SFF SFF-8431 [10]. Future OIF CEI-56G-VSR electrical specifications will apply. Figure 4-1 shows the recommended termination for these circuits. Alternate signaling logic are OTL3.4 and OTL4.10 which are specified in Reference [4]. Lane orientation and designation is specified in the pin-map tables given in Section 5.8.
The CFP2 module may optionally support loopback functionality. The capability to support the loopback functionality is dependent upon the interface IC technology, labeled as “Interface IC(s)” in the figure below. Recommended loopback orientation implementation is TX0 to RX0. The host loopback and the network loopback are oriented per Figure 4-2 shown below. The CFP MSA module vendor will specify which loopback functionality, if any, is supported. For details on controlling the loopback mode, please refer to Reference [7]. In optional loopback, TXn is looped back to RXn, for example TX0+ to RX0+, on both host and network side.
Figure 4-2: CFP2 Module Optional Loopback Orientation
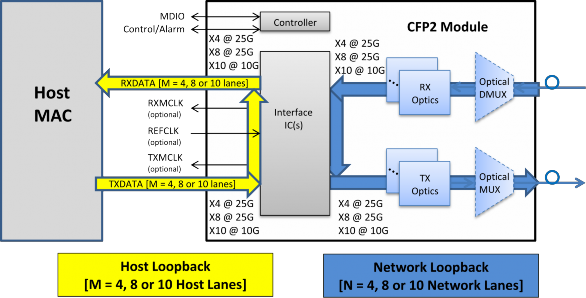
For M x 25 Gbit/s host electrical interface applications, the host may optionally supply a reference clock (REFCLK) at 1/160 electrical lane rate. The CFP2 module may optionally use the 1/160 reference clock or the 1/32 network lane rate clock recovered from the receiver path for transmitter path retiming, for example for Ethernet applications.
The host shall optionally supply a reference clock (REFCLK) at 1/40 electrical lane rate for M x 25 Gbit/s applications. The CFP2 module may optionally use the 1/40 reference clock for transmitter path retiming, for example for Telecom applications.
For M x 10 Gbit/s host electrical interface applications, the host may optionally supply a reference clock (REFCLK) at 1/64 electrical lane rate. The CFP2 module may optionally use the 1/64 reference clock for transmitter path retiming, for example for Ethernet applications.
The host may optionally supply a reference clock (REFCLK) at 1/16 electrical lane rate for M x 10 Gbit/s applications. The CFP2 module may optionally use the 1/16 reference clock for transmitter path retiming, for example for Telecom applications.
When provided, the REFCLK shall be CML differential AC-coupled and terminated within the CFP2 module as shown in Figure 4-1. There is no required phase relationship between the data lanes and the reference clock, but the clock frequency shall not deviate more than specified in Table 4-2. For detailed clock characteristics please refer to the below table.
Table 4-2: Optional Reference Clock Characteristics
Min. | Typ. | Max. | Unit | Notes | ||
Impedance | Zd | 80 | 100 | 120 | Ω | |
Frequency | ||||||
Frequency Stability |
f | -100 | 100 | ppm | For Ethernet applications; | |
-20 | 20 | For Telecom applications | ||||
Output Differential Voltage | VDIFF | 400 | 1200 | mV | Peak to Peak Differential | |
RMS Jitter6,7 |
| 10 | ps | Random Jitter. Over frequency band of 10kHz < f < 10MHz | ||
Clock Duty Cycle | 40 | 60 | % | |||
Clock Rise/Fall Time 10/90% | tr/f | 200 | 1250 | ps | 1/160 of electrical lane rate for M x 25 Gbit/s and 1/64 of electrical lane rate for M x 10 Gbit/s | |
50 | 315 | 1/40 of electrical lane rate for M x 25 Gbit/s and 1/16 of electrical lane rate for M x 10 Gbit/s |
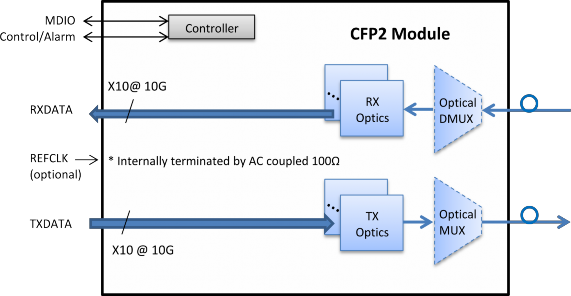
An example of CFP2 clocking for 4 x 25 Gbit/s applications is shown in Figure 4-3. An example of CFP2 clocking for 10 x 10 Gbit/s applications is shown in Figure 4-4.
Transmitter Monitor Clock (Option)
The CFP2 module may optionally supply a transmitter monitor clock for M x 25 Gbit/s applications. This option is not available for M x 10 Gbit/s applications. The transmitter monitor clock is intended to be used as a reference for measurements of the optical output. If provided, the clock shall operate at a rate relative to the optical network lane rate of 1/8 or 1/32 of 25 Gbit/s for 100 Gbit/s (4x25 Gbit/s, 8x25 Gbit/s) applications. Another option is a clock at 1/40 or 1/160 the rate of (host) transmitter electrical input data for M x 25 Gbit/s. Clock termination is shown in Figure 4-1. Detailed clock characteristics are specified in Table 4-3.
Receiver Monitor Clock (Option)
The CFP2 module may optionally supply a receiver monitor clock for M x 25 Gbit/s applications. This option is not available for M x 10 Gbit/s applications. The receiver monitor clock is intended to be used as a reference for measurements of the optical input. If provided, the clock shall operate at a rate relative to the optical network lane rate of 1/8 or 1/32 of 25 Gbit/s for 100 Gbit/s (4x25 Gbit/s, 8x25 Gbit/s) applications.
Another option is a clock at 1/40 or 1/160 the rate of (host) transmitter electrical input data for M x 25 Gbit/s. Clock termination is shown in Figure 4-1. Detailed clock characteristics are specified in Table 4-3.
![]()
6 The spectrum of the jitter within this frequency band is undefined. The CFP2 shall meet performance requirements with worst case condition of a single jitter tone of 10ps RMS at any frequency between 10 KHz and 10 MHz.
7 For Telecom applications better frequency may be required.
Table 4-3: Optional Transmitter & Receiver Monitor Clock Characteristics
Min. | Typ. | Max. | Unit | Notes | ||
Impedance | Zd | 80 | 100 | 120 | Ω | |
Frequency | ||||||
Output Differential Voltage | VDIFF | 400 | 1200 | mV | Peak to Peak Differential | |
Clock Duty Cycle | 40 | 60 | % | |||
Table 4-4: CFP2 Module Clocking Signals
Clock Name | Status | I/O | M x 25 Gbit/s Default Host Lane Rate | Optional rate | |
Datacom 100GBASE-SR4/LR4/ER4 | Telecom OTU4 | ||||
REFCLK | Optional | I | 1/160 (161.1328 MHz) or 1/40 (644.5313 MHz) | 1/160 (174.7031 MHz) | |
1/8 (3.22266 GHz) | 1/8 (3.49406 GHz) | ||||
or | or | ||||
TX_MCLK | 1/32 (805.665 MHz) | 1/32 (873.515 MHz) | |||
Optional | O | or | or | ||
RX_MCLK | 1/40 (644.5313 MHz) | 1/40 (698.8123 MHz) | |||
or | or | ||||
1/160 (161.1328 MHz) | 1/160 (174.7031 MHz) | ||||
M x 10 Gbit/s Default Host Lane Rate | |||||
Datacom | Datacom | ||||
Clock Name | Status | I/O | 100GBASE-LR4 100GBASE-SR10 | 40GBASE-FR Telecom | Optional rate |
40GBASE-SR4/LR4/ER4 | |||||
OTU4 | |||||
10x10GBASE-SR/LR | |||||
OC-768/STM-256,OTU3 | |||||
REFCLK | Optional | I | 1/64 of host lane rate (161.1328 MHz) | 1/64 of host lane rate (D : 161.1328 MHz) (T : 1xx MHz) | 1/16 of host lane rate (D : 644.5313 MHz) (T : 6xx MHz) |
TX_MCLK | Not Available | ||||
RX_MCLK | Not Available |
Note: Multi-protocol modules are recommended to adopt the clock rate used in Telecom applications.
Figure 4-3: Example of clocking for 4 x 25 Gbit/s CFP2 applications
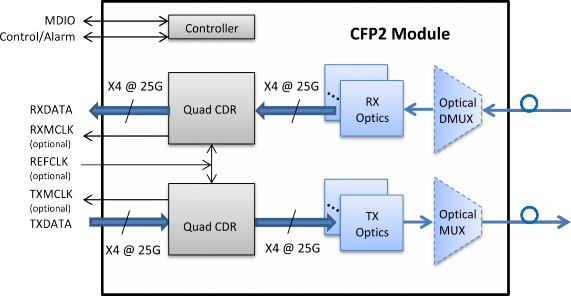
Figure 4-4: Example of clocking for 10 x 10 Gbit/s CFP2 applications
![]()
![]()
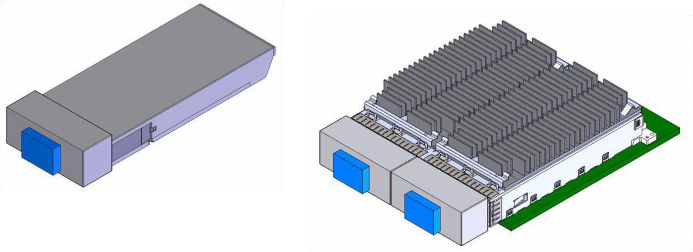
The CFP2 module is designed to be plugged into a host cage assembly with a riding heat sink. The cage assembly is fabricated within the host system and the CFP2 module may be inserted at a later time. Shown in Figure 5-1 is a drawing of the CFP2 module and CFP2 modules inserted into a host dual-port cage system with a riding heat sink.
Figure 5-1: CFP2 Module & CFP2 Module Mated in Host Dual Port System
Starting in Figure 5-2 is an overview of the CFP2 mechanical assembly with subsequent figures showing the constituent elements in greater detail. The detailed dimensions are located in a separate design document hosted on the CFP MSA Website (www.cfp-msa.org).
Figure 5-2: Host Cage System and Mounting Method Overview

* Other mounting options are possible.
The CFP2 MSA specifies a two piece electrical connector for superior electrical performance and superior mechanical integrity. Shown in Figure 5-3 is the module plug connector assembly which is contained as a sub-component within the CFP2 module.
Figure 5-3: CFP2 Module Plug Connector Assembly
The CFP2 MSA specifies a two piece electrical connector for superior electrical performance and superior mechanical integrity. Shown in Figure 5-4 and Figure 5-5 are overview drawings of the host connector and cover assemblies. These assemblies shall be built into the host system. The Host Connector shall be covered by the Host Connector Cover Assembly which provides electromagnetic shielding.
The Host Connector cover includes gaskets around the connector cover openings for the module plug connector. These gaskets provide electromagnetic shielding between the module and host connector for improved electromagnetic performance. Specifications for the connector cover gaskets are not given in this MSA but are to be provided by the host electrical connector component supplier.
This MSA does specify the host connector cover gasket shall meet a minimum peel strength of 12 N/cm (7 lbs/in).
Figure 5-4: CFP2 Dual Port Host Connector Cover Assembly
Figure 5-5: CFP2 Host Connector Assembly
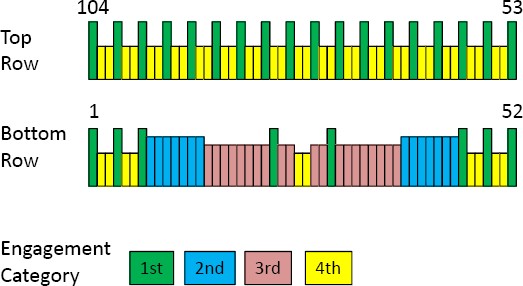
The module plug connector has a physical offset of metal contact pins to insure that certain signals make engagement between the module and host prior to other signals. There are four categories of pin engagement. A map of the connector engagement is shown in Figure 5-6. The connector pin map engagement order is guaranteed by the physical offset built into the module plug connector. The host connector has all contacts on the same plane without offset.
Figure 5-6: CFP2 Pin Map Connector Engagement
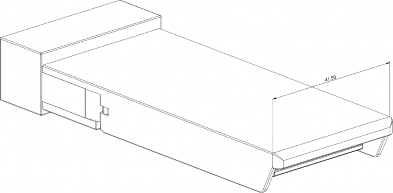
An overview of the CFP2 module dimensions is show in the below Figure 5-7. The CFP2 maximum header height is specified as shown in Figure 5-7. A low-profile header height option is specified to accommodate narrow host front panel designs. The detailed CFP2 module dimensions are located in a separate document hosted on the CFP MSA Website (www.cfp-msa.org). All mechanical hardware dimensions in this document are for reference only. Normative dimensions are found in the latest published CFP2 baseline drawing.
Figure 5-7: CFP2 Module Dimension Overview
![]()

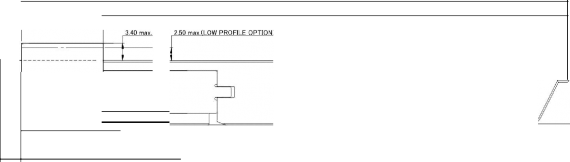
1. min.
4.10 max. OPTICAL CONNECTOR PROTRUSION
107.50
![]()
CFP2 Mechanical Surface Characteristics
The mechanical surface of flat top CFP2 module which may be in contact with the host riding heat sink assembly shall be compliant with specifications in Table 5-1. The parameters listed in Table 5-1 define the CFP2 module thermal interface and may be used by host system designers to specify the host cage assembly opening and riding heat sink for optimizing host system thermal management performance.
Surface flatness and roughness parameters are specified per CFP2 module power class (see Table 2-2) to allow for optimization of module thermal performance and cost. Non-compliance to these specifications may cause significant thermal performance degradation. Only the top surface of the module is assumed to be used for heat transfer.
Table 5-1: CFP2 Mechanical Characteristics
Parameters | Power Class | Max. | Unit | Notes |
Weight | 1 - 4 | 210 | g | |
Flatness | 1 | 0.15 | mm | |
2 | 0.15 | mm | ||
3 | 0.12 | mm | ||
4 | 0.12 | mm | ||
Roughness | 1 | 3.2 | Ra | |
2 | 3.2 | Ra | ||
3 | 1.6 | Ra | ||
4 | 1.6 | Ra | ||
Temperature Delta | 1 - 4 | 7 | °C | No heat sink; 200 lfm sideways airflow |
Normal force exerted on module | 1 - 4 | 15 | N | Heat sink on module top surface |
As described in Section 1.3.1, the CFP2 module shall be hot pluggable. A consequence of the CFP2 module being hot pluggable is that an end user be equipped to insert and extract the module in the field. The required forces are specified below in Table 5-2.
Table 5-2: CFP2 Module Insertion, Extraction Forces
Max. | Unit | Notes | |
Maximum Insertion Force | 80 | N | Without Heat Sink |
Maximum Extraction Force | 50 | N | Without Heat Sink |
Minimum Module Retention Force | 90 | N | No damage to module below 90 N |
Minimum Cage Retention Force | 180 | N | No damage to cage latch below 180 N |
Minimum rating for host/module connector insertion/extraction is 200 cycles.
* Typical increase in those forces by adding heat sink is below 5N.
The detailed CFP2 host system dimensions including host board layout are located in a separate document hosted on the CFP MSA Website (www.cfp-msa.org).
The riding heat sink and host cage top surface designs given in the latest published CFP2 baseline drawing are only exemplary and are not required for compliance with the CFP2 MSA. Cage opening and heat sink specifications vary with host system design and thermal performance requirements. The heat sink/cage designs are therefore host system dependent and may be optimized by the system designer.
The riding heat sink illustrated in Figure 5-8 is for example only. The recommended material for the heat sink is aluminum. Furthermore, a thermal interposer for reduced friction is recommended to be used on the underside of the riding heat sink.
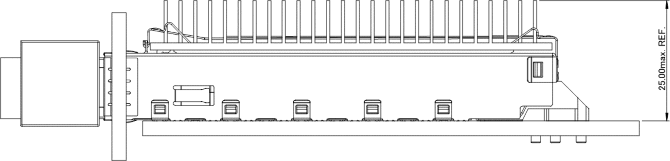
The mounting dimensions for the Riding Heat Sink are shown below in Figure 5-9. The actual dimensions of the heat sink and cage top opening may be optimized for the particular host system.
Figure 5-9: Host Cage Top Surface Opening
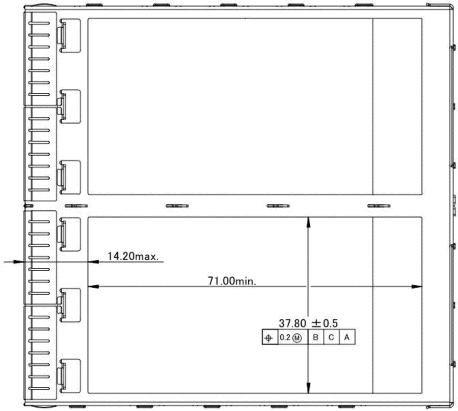
The CFP2 module shall support LC, MTP12 and MTP24 optical connector types, as listed in Table 5-3. The optical connectors are positioned in the CFP2 module as illustrated in Figure 5-10. The optical connector is centered in position along the X-axis (module width) with an offset tolerance of ±0.5mm. The position of the optical connector in the Y and Z axes shall be specified by the CFP2 module manufacturer.
Table 5-3: Optical Connectors8
Pin # | Category | Reference Number |
LC Connector | TBA | TBA |
MPO12 Connector | TBA | TBA |
MPO24 Connector | TBA | TBA |
![]()
8 Other optical connectors may be supported
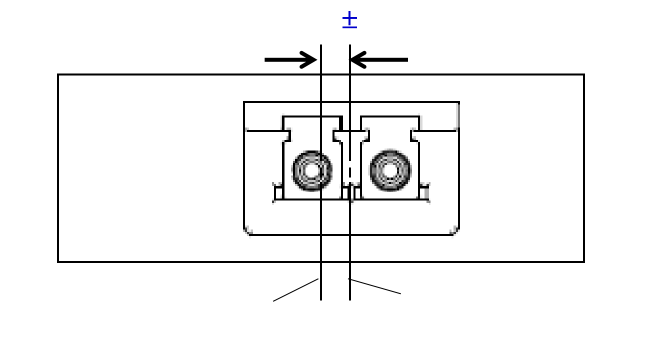
Offset 2mm
Figure 5-10: CFP2 Optical Connector Position
Optional Optical LC Connector Position for Telecom Applications
This option, described in Reference [1], is not supported in the first release of the CFP2 module MSA, but may be specified in a future release.
CFP2 host electrical connector supplier information will be added to Table 5-4 in a future release of this MSA.
Table 5-4 CFP2 Host Connector Assembly
Part Number | Supplier | Part Name |
TBA | TBA | Cage |
TBA | TBA | Host Connector Cover Assembly |
TBA | TBA | Host Connector |
The CFP2 connector has 104 pins which are arranged in Top and Bottom rows. The CFP2 connector supports the following configurations:
Four (4) 25Gbit/s TX lanes plus four 25Gbit/s RX lanes;
Eight (8) 25Gbit/s TX lanes plus eight 25Gbit/s RX lanes;
Ten (10) 10Gbit/s TX lanes plus ten 10Gbit/s RX lanes.
The CFP2 connector top row and bottom row pin assignments for the N x 25Gbit/s and the 10 x 10Gbit/s configurations are illustrated in Table 5- and Table 5-6, respectively. Detailed description of the bottom row pins 1 through pin 52 are given in Table 5-7 and Table 5-8. Note the REFCLK pins are located on the top row along with the high-speed TX and RX data pins. A single-ended REFCLK is an option. The CFP2 connector pin map orientation is shown in Figure 5-11.
Figure 5-11: CFP2 Connector Pin Map Orientation

I
\
/
•
I
\
•
'
.
-
-
I
\
....
-
\
I
\
I
Table 5-5: CFP2 N x 25 Gbit/s Pin-Map
Pin view from top ==> Host
Bottom (Nx25G) | |
1 | GND |
2 | (TX_MCLKn) |
3 | (TX_MCLKp) |
4 | GND |
5 | N.C. |
6 | N.C. |
7 | 3.3V_GND |
8 | 3.3V_GND |
9 | 3.3V |
10 | 3.3V |
11 | 3.3V |
12 | 3.3V |
13 | 3.3V_GND |
14 | 3.3V_GND |
15 | VND_IO_A |
16 | VND_IO_B |
17 | PRG_CNTL1 |
18 | PRG_CNTL2 |
19 | PRG_CNTL3 |
20 | PRG_ALRM1 |
21 | PRG_ALRM2 |
22 | PRG_ALRM3 |
23 | GND |
24 | TX_DIS |
25 | RX_LOS |
26 | MOD_LOPWR |
27 | MOD_ABS |
28 | MOD_RSTn |
29 | GLB_ALRMn |
30 | GND |
31 | MDC |
32 | MDIO |
33 | PRTADR0 |
34 | PRTADR1 |
35 | PRTADR2 |
36 | VND_IO_C |
37 | VND_IO_D |
38 | VND_IO_E |
39 | 3.3V_GND |
40 | 3.3V_GND |
41 | 3.3V |
42 | 3.3V |
43 | 3.3V |
44 | 3.3V |
45 | 3.3V_GND |
46 | 3.3V_GND |
47 | N.C. |
48 | N.C. |
49 | GND |
50 | (RX_MCLKn) |
51 | (RX_MCLKp) |
52 | GND |
Top (4x25G) | |
104 | GND |
103 | N.C. |
102 | N.C. |
101 | GND |
100 | TX3n |
99 | TX3p |
98 | GND |
97 | TX2n |
96 | TX2p |
95 | GND |
94 | N.C. |
93 | N.C. |
92 | GND |
91 | N.C. |
90 | N.C. |
89 | GND |
88 | TX1n |
87 | TX1p |
86 | GND |
85 | TX0n |
84 | TX0p |
83 | GND |
82 | N.C. |
81 | N.C. |
80 | GND |
79 | (REFCLKn) |
78 | (REFCLKp) |
77 | GND |
76 | N.C. |
75 | N.C. |
74 | GND |
73 | RX3n |
72 | RX3p |
71 | GND |
70 | RX2n |
69 | RX2p |
68 | GND |
67 | N.C. |
66 | N.C. |
65 | GND |
64 | N.C. |
63 | N.C. |
62 | GND |
61 | RX1n |
60 | RX1p |
59 | GND |
58 | RX0n |
57 | RX0p |
56 | GND |
55 | N.C. |
54 | N.C. |
53 | GND |
Top (8x25G) |
GND |
TX7n |
TX7p |
GND |
TX6n |
TX6p |
GND |
TX5n |
TX5p |
GND |
TX4n |
TX4p |
GND |
TX3n |
TX3p |
GND |
TX2n |
TX2p |
GND |
TX1n |
TX1p |
GND |
TX0n |
TX0p |
GND |
(REFCLKn) |
(REFCLKp) |
GND |
RX7n |
RX7p |
GND |
RX6n |
RX6p |
GND |
RX5n |
RX5p |
GND |
RX4n |
RX4p |
GND |
RX3n |
RX3p |
GND |
RX2n |
RX2p |
GND |
RX1n |
RX1p |
GND |
RX0n |
RX0p |
GND |
`
REFCLK
(Optional)
Table 5-6: CFP2 10 x 10 Gbit/s Pin-Map
Pin view from top ==> Host
CFP2 | |
Bottom | |
1 | GND |
2 | TX9n |
3 | TX9p |
4 | GND |
5 | TX8n |
6 | TX8p |
7 | GND |
8 | 3.3V_GND |
9 | 3.3V |
10 | 3.3V |
11 | 3.3V |
12 | 3.3V |
13 | 3.3V_GND |
14 | 3.3V_GND |
15 | VND_IO_A |
16 | VND_IO_B |
17 | PRG_CNTL1 |
18 | PRG_CNTL2 |
19 | PRG_CNTL3 |
20 | PRG_ALRM1 |
21 | PRG_ALRM2 |
22 | PRG_ALRM3 |
23 | GND |
24 | TX_DIS |
25 | RX_LOS |
26 | MOD_LOPWR |
27 | MOD_ABS |
28 | MOD_RSTn |
29 | GLB_ALRMn |
30 | GND |
31 | MDC |
32 | MDIO |
33 | PRTADR0 |
34 | PRTADR1 |
35 | PRTADR2 |
36 | VND_IO_C |
37 | VND_IO_D |
38 | VND_IO_E |
39 | 3.3V_GND |
40 | 3.3V_GND |
41 | 3.3V |
42 | 3.3V |
43 | 3.3V |
44 | 3.3V |
45 | 3.3V_GND |
46 | GND |
47 | RX9n |
48 | RX9p |
49 | GND |
50 | RX8n |
51 | RX8p |
52 | GND |
CFP2 | |
Top | |
104 | GND |
103 | TX7n |
102 | TX7p |
101 | GND |
100 | TX6n |
99 | TX6p |
98 | GND |
97 | TX5n |
96 | TX5p |
95 | GND |
94 | TX4n |
93 | TX4p |
92 | GND |
91 | TX3n |
90 | TX3p |
89 | GND |
88 | TX2n |
87 | TX2p |
86 | GND |
85 | TX1n |
84 | TX1p |
83 | GND |
82 | TX0n |
81 | TX0p |
80 | GND |
79 | (REFCLKn) |
78 | (REFCLKp) |
77 | GND |
76 | RX7n |
75 | RX7p |
74 | GND |
73 | RX6n |
72 | RX6p |
71 | GND |
70 | RX5n |
69 | RX5p |
68 | GND |
67 | RX4n |
66 | RX4p |
65 | GND |
64 | RX3n |
63 | RX3p |
62 | GND |
61 | RX2n |
60 | RX2p |
59 | GND |
58 | RX1n |
57 | RX1p |
56 | GND |
55 | RX0n |
54 | RX0p |
53 | GND |
`
REFCLK
(Optional)
Table 5-7: CFP2 Multi-Port Pin-Map
CFP2 | |
Bottom | |
1 | GND |
2 | S3_TXn |
3 | S3_TXp |
4 | GND |
5 | S2_TXn |
6 | S2_TXp |
7 | GND |
8 | 3.3V_GND |
9 | 3.3V |
10 | 3.3V |
11 | 3.3V |
12 | 3.3V |
13 | 3.3V_GND |
14 | 3.3V_GND |
15 | VND_IO_A |
16 | VND_IO_B |
17 | PRG_CNTL1 |
18 | PRG_CNTL2 |
19 | PRG_CNTL3 |
20 | PRG_ALRM1 |
21 | PRG_ALRM2 |
22 | PRG_ALRM3 |
23 | GND |
24 | TX_DIS |
25 | RX_LOS |
26 | MOD_LOPWR |
27 | MOD_ABS |
28 | MOD_RSTn |
29 | GLB_ALRMn |
30 | GND |
31 | MDC |
32 | MDIO |
33 | PRTADR0 |
34 | PRTADR1 |
35 | PRTADR2 |
36 | VND_IO_C |
37 | VND_IO_D |
38 | VND_IO_E |
39 | 3.3V_GND |
40 | 3.3V_GND |
41 | 3.3V |
42 | 3.3V |
43 | 3.3V |
44 | 3.3V |
45 | 3.3V_GND |
46 | GND |
47 | S3_RXn |
48 | S3_RXp |
49 | GND |
50 | S2_RXn |
51 | S2_RXp |
52 | GND |
CFP2 | |
Top | |
104 | GND |
103 | S1_TX3n |
102 | S1_TX3p |
101 | GND |
100 | S1_TX2n |
99 | S1_TX2p |
98 | GND |
97 | S1_TX1n |
96 | S1_TX1p |
95 | GND |
94 | S1_TX0n |
93 | S1_TX0p |
92 | GND |
91 | TX3n |
90 | TX3p |
89 | GND |
88 | TX2n |
87 | TX2p |
86 | GND |
85 | TX1n |
84 | TX1p |
83 | GND |
82 | TX0n |
81 | TX0p |
80 | GND |
79 | (REFCLKn) |
78 | (REFCLKp) |
77 | GND |
76 | S1_RX3n |
75 | S1_RX3p |
74 | GND |
73 | S1_RX2n |
72 | S1_RX2p |
71 | GND |
70 | S1_RX1n |
69 | S1_RX1p |
68 | GND |
67 | S1_RX0n |
66 | S1_RX0p |
65 | GND |
64 | RX3n |
63 | RX3p |
62 | GND |
61 | RX2n |
60 | RX2p |
59 | GND |
58 | RX1n |
57 | RX1p |
56 | GND |
55 | RX0n |
54 | RX0p |
53 | GND |
Pin view from top ==> Host
`
REFCLK
(Optional)
Table 5-8: CFP2 Bottom Row Pin Description for N x 25 Gbit/s applications
PIN # | NAME | I/O | Logic | Description |
1 | GND | |||
2 | (TX_MCLKn) | O | CML | For optical waveform testing. Not for normal use. |
3 | (TX_MCLKp) | O | CML | For optical waveform testing. Not for normal use. |
4 | GND | |||
5 | N.C | No Connect | ||
6 | N.C. | |||
7 | 3.3V_GND | 3.3V Module Supply Voltage Return Ground, can be separate or tied together with Signal Ground | ||
8 | 3.3V_GND | |||
9 | 3.3V | 3.3V Module Supply Voltage | ||
10 | 3.3V | |||
11 | 3.3V | |||
12 | 3.3V | |||
13 | 3.3V_GND | |||
14 | 3.3V_GND | |||
15 | VND_IO_A | I/O | Module Vendor I/O A. Do Not Connect! | |
16 | VND_IO_B | I/O | Module Vendor I/O B. Do Not Connect! | |
17 | PRG_CNTL1 | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Programmable Control 1 set over MDIO, MSA Default: TRXIC_RSTn, TX & RX ICs reset, "0": reset, "1" or NC: enabled = not used |
18 | PRG_CNTL2 | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Programmable Control 2 set over MDIO, MSA Default: Hardware Interlock LSB, "00": ≤3W, "01": ≤6W, "10": ≤9W, "11" or NC: ≤12W = not used |
19 | PRG_CNTL3 | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Programmable Control 3 set over MDIO, MSA Default: Hardware Interlock MSB, "00": ≤3W, "01": ≤6W, "10": ≤9W, "11" or NC: ≤12W = not used |
20 | PRG_ALRM1 | O | LVCMOS | Programmable Alarm 1 set over MDIO, MSA Default: HIPWR_ON, "1": module power up completed, "0": module not high powered up |
21 | PRG_ALRM2 | O | LVCMOS | Programmable Alarm 2 set over MDIO, MSA Default: MOD_READY, "1": Ready, "0": not Ready. |
22 | PRG_ALRM3 | O | LVCMOS | Programmable Alarm 3 set over MDIO, MSA Default: MOD_FAULT, fault detected, "1": Fault, "0": No Fault |
23 | GND | |||
24 | TX_DIS | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Transmitter Disable for all lanes, "1" or NC = transmitter disabled, "0" = transmitter enabled |
25 | RX_LOS | O | LVCMOS | Receiver Loss of Optical Signal, "1": low optical signal, "0": normal condition |
PIN # | NAME | I/O | Logic | Description |
26 | MOD_LOPWR | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Module Low Power Mode. "1" or NC: module in low power (safe) mode, "0": power-on enabled |
27 | MOD_ABS | O | GND | Module Absent. "1" or NC: module absent, "0": module present, Pull Up Resistor on Host |
28 | MOD_RSTn | I | LVCMOS w/ PDR | Module Reset. "0" resets the module, "1" or NC = module enabled, Pull Down Resistor in Module |
29 | GLB_ALRMn | O | LVCMOS | Global Alarm. “0": alarm condition in any MDIO Alarm register, "1": no alarm condition, Open Drain, Pull Up Resistor on Host |
30 | GND | |||
31 | MDC | I | 1.2V CMOS | Management Data Clock (electrical specs as per IEEE Std 802.3-2012) |
32 | MDIO | I/O | 1.2V CMOS | Management Data I/O bi-directional data (electrical specs as per IEEE Std 802.3-2012) |
33 | PRTADR0 | I | 1.2V CMOS | MDIO Physical Port address bit 0 |
34 | PRTADR1 | I | 1.2V CMOS | MDIO Physical Port address bit 1 |
35 | PRTADR2 | I | 1.2V CMOS | MDIO Physical Port address bit 2 |
36 | VND_IO_C | I/O | Module Vendor I/O C. Do Not Connect! | |
37 | VND_IO_D | I/O | Module Vendor I/O D. Do Not Connect! | |
38 | VND_IO_E | I/O | Module Vendor I/O E. Do Not Connect! | |
39 | 3.3V_GND | |||
40 | 3.3V_GND | |||
41 | 3.3V | 3.3V Module Supply Voltage | ||
42 | 3.3V | |||
43 | 3.3V | |||
44 | 3.3V | |||
45 | 3.3V_GND | |||
46 | 3.3V_GND | |||
47 | N.C | No Connect | ||
48 | N.C. | |||
49 | GND | |||
50 | (RX_MCLKn) | O | CML | For optical waveform testing. Not for normal use. |
51 | (RX_MCLKp) | O | CML | For optical waveform testing. Not for normal use. |
52 | GND |
Table 5-9: CFP2 Bottom Row Pin Description for 10 x 10 Gbit/s applications
PIN # | NAME | I/O | Logic | Description |
1 | GND | |||
2 | TX9n | I | CML | Transmit data input |
3 | TX9p | I | CML | Transmit data input |
4 | GND | |||
5 | TX8n | I | CML | Transmit data input |
6 | TX8p | I | CML | Transmit data input |
7 | GND | 3.3V Module Supply Voltage Return Ground, can be separate or tied together with Signal Ground | ||
8 | 3.3V_GND | |||
9 | 3.3V | 3.3V Module Supply Voltage | ||
10 | 3.3V | |||
11 | 3.3V | |||
12 | 3.3V | |||
13 | 3.3V_GND | |||
14 | 3.3V_GND | |||
15 | VND_IO_A | I/O | Module Vendor I/O A. Do Not Connect! | |
16 | VND_IO_B | I/O | Module Vendor I/O B. Do Not Connect! | |
17 | PRG_CNTL1 | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Programmable Control 1 set over MDIO, MSA Default: TRXIC_RSTn, TX & RX ICs reset, "0": reset, "1" or NC: enabled = not used |
18 | PRG_CNTL2 | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Programmable Control 2 set over MDIO, MSA Default: Hardware Interlock LSB, "00": ≤3W, "01": ≤6W, "10": ≤9W, "11" or NC: ≤12W = not used |
19 | PRG_CNTL3 | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Programmable Control 3 set over MDIO, MSA Default: Hardware Interlock MSB, "00": ≤3W, "01": ≤6W, "10": ≤9W, "11" or NC: ≤12W = not used |
20 | PRG_ALRM1 | O | LVCMOS | Programmable Alarm 1 set over MDIO, MSA Default: HIPWR_ON, "1": module power up completed, "0": module not high powered up |
21 | PRG_ALRM2 | O | LVCMOS | Programmable Alarm 2 set over MDIO, MSA Default: MOD_READY, "1": Ready, "0": not Ready. |
22 | PRG_ALRM3 | O | LVCMOS | Programmable Alarm 3 set over MDIO, MSA Default: MOD_FAULT, fault detected, "1": Fault, "0": No Fault |
23 | GND | |||
24 | TX_DIS | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Transmitter Disable for all lanes, "1" or NC = transmitter disabled, "0" = transmitter enabled |
25 | RX_LOS | O | LVCMOS | Receiver Loss of Optical Signal, "1": low optical signal, "0": normal condition |
PIN # | NAME | I/O | Logic | Description |
26 | MOD_LOPWR | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Module Low Power Mode. "1" or NC: module in low power (safe) mode, "0": power-on enabled |
27 | MOD_ABS | O | GND | Module Absent. "1" or NC: module absent, "0": module present, Pull Up Resistor on Host |
28 | MOD_RSTn | I | LVCMOS w/ PDR | Module Reset. "0" resets the module, "1" or NC = module enabled, Pull Down Resistor in Module |
29 | GLB_ALRMn | O | LVCMOS | Global Alarm. “0": alarm condition in any MDIO Alarm register, "1": no alarm condition, Open Drain, Pull Up Resistor on Host |
30 | GND | |||
31 | MDC | I | 1.2V CMOS | Management Data Clock (electrical specs as per IEEE Std 802.3-2012) |
32 | MDIO | I/O | 1.2V CMOS | Management Data I/O bi-directional data (electrical specs as per IEEE Std 802.3-2012) |
33 | PRTADR0 | I | 1.2V CMOS | MDIO Physical Port address bit 0 |
34 | PRTADR1 | I | 1.2V CMOS | MDIO Physical Port address bit 1 |
35 | PRTADR2 | I | 1.2V CMOS | MDIO Physical Port address bit 2 |
36 | VND_IO_C | I/O | Module Vendor I/O C. Do Not Connect! | |
37 | VND_IO_D | I/O | Module Vendor I/O D. Do Not Connect! | |
38 | VND_IO_E | I/O | Module Vendor I/O E. Do Not Connect! | |
39 | 3.3V_GND | |||
40 | 3.3V_GND | |||
41 | 3.3V | 3.3V Module Supply Voltage | ||
42 | 3.3V | |||
43 | 3.3V | |||
44 | 3.3V | |||
45 | 3.3V_GND | |||
46 | GND | |||
47 | RX9n | O | CML | Received data output |
48 | RX9p | O | CML | Received data output |
49 | GND | |||
50 | RX8n | O | CML | Received data output |
51 | RX8p | O | CML | Received data output |
52 | GND |
Table 5-10: CFP2 Bottom Row Pin Description for Multi-Port applications
PIN # | NAME | I/O | Logic | Description |
1 | GND | |||
2 | S3_TXn | I | CML | Transmit data input |
3 | S3_TXp | I | CML | Transmit data input |
4 | GND | |||
5 | S2_TXn | I | CML | Transmit data input |
6 | S2_TXp | I | CML | Transmit data input |
7 | GND | 3.3V Module Supply Voltage Return Ground, can be separate or tied together with Signal Ground | ||
8 | 3.3V_GND | |||
9 | 3.3V | 3.3V Module Supply Voltage | ||
10 | 3.3V | |||
11 | 3.3V | |||
12 | 3.3V | |||
13 | 3.3V_GND | |||
14 | 3.3V_GND | |||
15 | VND_IO_A | I/O | Module Vendor I/O A. Do Not Connect! | |
16 | VND_IO_B | I/O | Module Vendor I/O B. Do Not Connect! | |
17 | PRG_CNTL1 | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Programmable Control 1 set over MDIO, MSA Default: TRXIC_RSTn, TX & RX ICs reset, "0": reset, "1" or NC: enabled = not used |
18 | PRG_CNTL2 | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Programmable Control 2 set over MDIO, MSA Default: Hardware Interlock LSB, "00": ≤3W, "01": ≤6W, "10": ≤9W, "11" or NC: ≤12W = not used |
19 | PRG_CNTL3 | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Programmable Control 3 set over MDIO, MSA Default: Hardware Interlock MSB, "00": ≤3W, "01": ≤6W, "10": ≤9W, "11" or NC: ≤12W = not used |
20 | PRG_ALRM1 | O | LVCMOS | Programmable Alarm 1 set over MDIO, MSA Default: HIPWR_ON, "1": module power up completed, "0": module not high powered up |
21 | PRG_ALRM2 | O | LVCMOS | Programmable Alarm 2 set over MDIO, MSA Default: MOD_READY, "1": Ready, "0": not Ready. |
22 | PRG_ALRM3 | O | LVCMOS | Programmable Alarm 3 set over MDIO, MSA Default: MOD_FAULT, fault detected, "1": Fault, "0": No Fault |
23 | GND | |||
24 | TX_DIS | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Transmitter Disable for all lanes, "1" or NC = transmitter disabled, "0" = transmitter enabled |
25 | RX_LOS | O | LVCMOS | Receiver Loss of Optical Signal, "1": low optical signal, "0": normal condition |
PIN # | NAME | I/O | Logic | Description |
26 | MOD_LOPWR | I | LVCMOS w/ PUR | Module Low Power Mode. "1" or NC: module in low power (safe) mode, "0": power-on enabled |
27 | MOD_ABS | O | GND | Module Absent. "1" or NC: module absent, "0": module present, Pull Up Resistor on Host |
28 | MOD_RSTn | I | LVCMOS w/ PDR | Module Reset. "0" resets the module, "1" or NC = module enabled, Pull Down Resistor in Module |
29 | GLB_ALRMn | O | LVCMOS | Global Alarm. “0": alarm condition in any MDIO Alarm register, "1": no alarm condition, Open Drain, Pull Up Resistor on Host |
30 | GND | |||
31 | MDC | I | 1.2V CMOS | Management Data Clock (electrical specs as per IEEE Std 802.3-2012) |
32 | MDIO | I/O | 1.2V CMOS | Management Data I/O bi-directional data (electrical specs as per IEEE Std 802.3-2012) |
33 | PRTADR0 | I | 1.2V CMOS | MDIO Physical Port address bit 0 |
34 | PRTADR1 | I | 1.2V CMOS | MDIO Physical Port address bit 1 |
35 | PRTADR2 | I | 1.2V CMOS | MDIO Physical Port address bit 2 |
36 | VND_IO_C | I/O | Module Vendor I/O C. Do Not Connect! | |
37 | VND_IO_D | I/O | Module Vendor I/O D. Do Not Connect! | |
38 | VND_IO_E | I/O | Module Vendor I/O E. Do Not Connect! | |
39 | 3.3V_GND | |||
40 | 3.3V_GND | |||
41 | 3.3V | 3.3V Module Supply Voltage | ||
42 | 3.3V | |||
43 | 3.3V | |||
44 | 3.3V | |||
45 | 3.3V_GND | |||
46 | GND | |||
47 | S3_RXn | O | CML | Received data output |
48 | S3_RXp | O | CML | Received data output |
49 | GND | |||
50 | S2_RXn | O | CML | Received data output |
51 | S2_RXp | O | CML | Received data output |
52 | GND |
CFP2 Bail Latch Color Coding and Labeling
Table 5-11: CFP2 Bail Latch Color Coding
Bail Latch Color Minimum reach & Minimum loss | Bail Latch Band | |||
10G/fiber One center black band (010) | 25G/fiber (or 20G/fiber) Two side black bands (101) | 50G/fiber (or 40G/fiber) Three black bands (111) | 100G/fiber No bands (solid color) (000) | |
Beige 100m & 2dB (MMF) | 100GE-SR10 Mx 40GE-SR4 Nx 10GE-SR | 100GE-SR4 | Mx “40GE-SR”* | “100GE-SR”* |
Yellow 500m & 2.5dB (SMF) | “40GE-nR4”* parallel | “100GE-nR4”* parallel | “100GE-nR2”* parallel | “100GE-nR4”* |
Green 2km & 4dB (SMF) | “100GE-FR4”* parallel | Mx 40GE-FR | “100GE-FR4”* | |
Lighter Blue 10km & 6dB | Nx 10GE-LR | Mx 40GE-LR4 | 100GE-LR4 | |
Lighter Red 30km/40km | Nx 10GE-ER | 100G DD DWDM | Mx 40GE-ER4 | 100GE-ER4 |
White ≤ 80km | Nx “10GE-ZR”* | 100G DD DWDM | Mx “40GE-ZR4”* | “100GE-ZR4”* 100G Coh. DWDM |
Note 1: Link budget = Minimum penalty [function of minimum reach] + minimum loss Note 2: * For potential future application; Not currently a standard nor MSA.
Note 3: Bail latch without any color (including no black bands; metal only) indicates a module that does not fit into any of the defined categories.
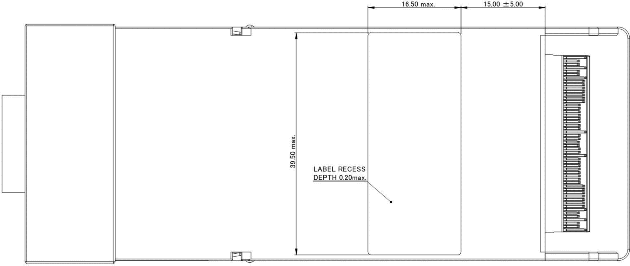
The CFP2 module should be clearly labeled. The complete labeling need not be visible when the CFP2 module is installed in the host cage assembly. A recessed area on the bottom of the CFP2 module, as shown in Figure 5-12, is the recommended location for module label.
Figure 5-12: CFP2 Module Label Recess
![]()
![]()
Per Reference [1].
End of Document